The aluminum smelting furnace can be divided into two basic types-round smelting furnace and rectangular smelting furnace. Both types of aluminum smelting furnaces can be built into a fixed or tilting type. Whether to build a fixed or tilting furnace depends mainly on the equipment’s budget and operation.
If the smelting plant can build grounds of different heights, the foundation conditions required for the installation of a fixed furnace are much simpler. Due to the furnace discharge port, the location of the melting furnace in the workshop will be higher than that of the holding furnace and casting machine. This situation requires the construction of a spacious ramp dedicated to vehicles, which occupies a lot of space.
To build a tilting furnace, you must consider the high requirements for the foundation, as well as the furnace tilting mechanism, the liquid aluminum conveying system, etc. In this case, the investment and maintenance costs will increase. However, the tilting furnace can make the melting and casting workshop layout more reasonable, and all equipment can be installed on the same plane of the workshop. The tipping furnace also has the advantages of fast and convenient transportation of liquid aluminum, which is very suitable for the needs of the melting and casting plant to adjust the alloy varieties frequently. The tilting mechanism can easily adjust the conveying speed of the liquid metal, thereby accurately controlling the level of the metal in the launder, which is very important for subsequent casting production.
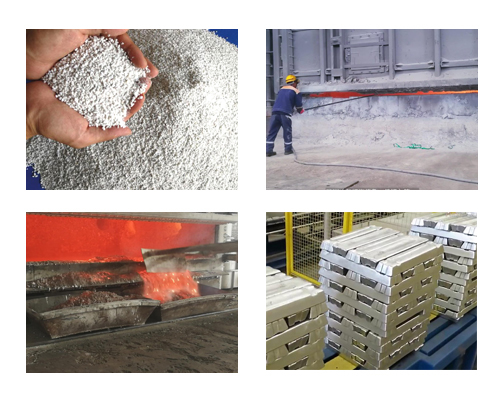

The aluminum smelting furnace is an important place for flux refining. Fluxes are widely used in the production of primary aluminum and secondary aluminum to improve the quality of the melt and the recovery rate of metal aluminum.
Aluminum Casting Fluxes Advantage
- Changing the wettability of the aluminum melt to the oxides, makes the aluminum melt easy to separate from the oxides, so that most of the oxides enter the flux and reduce the oxide content in the melt.
- The flux can change the state of the surface oxide film on the melt. This is because it can break the solid and dense oxide film on the surface of the melt into fine particles, which is beneficial for the hydrogen in the melt to permeate and escape from the particle gaps of the oxide film and enter the atmosphere.
- The presence of the flux layer can prevent the contact of water vapor in the atmosphere with the aluminum melt, make it difficult for hydrogen to enter the aluminum melt, and prevent the melt from oxidizing and burning.
- The flux can absorb the oxides in the aluminum melt, so that the melt can be purified.